Linear Optical Encoders: Understanding the Working PrincipleLinear
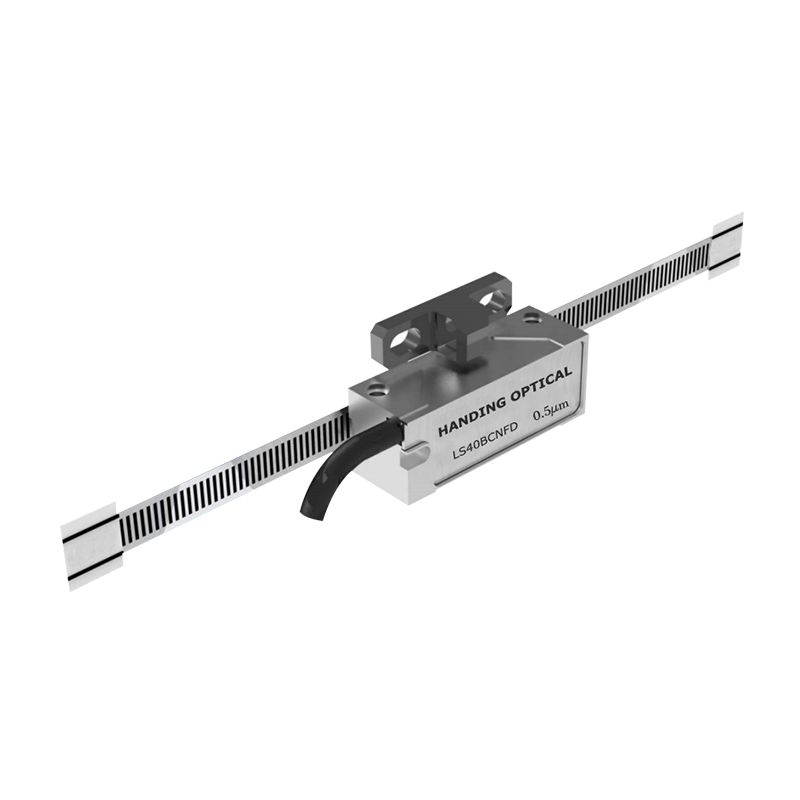

Optical Encoders are high-precision devices used for encoding linear movement into an electrical signal. These encoders use the principle of optical interference to produce accurate, consistent measurements of linear displacement. Linear Optical Encoders are widely used in industries such as robotics, automation, and manufacturing. In this article, we will discuss the working principle of Linear Optical Encoders and their advantages and applications.
Working Principle of Linear Optical Encoders
A Linear Optical Encoder typically consists of a scale and a reader head. The scale is a thin strip of material that has a series of evenly spaced, parallel lines or bars that are etched or printed on the surface. The reader head contains a light source and several photodetectors. As the scale moves, the light from the source passes through the lines and bars of the scale, creating a pattern of light and dark areas. This pattern is picked up by the photodetectors and converted into a digital signal that corresponds to the position of the reader head on the scale.
The scales used in Linear Optical Encoders can be of different types, such as open optical encoders and exposed linear encoders. Open optical encoders have a transparent or translucent scale that allows light to pass through, while exposed linear encoders have a reflective surface that reflects the light back to the reader head.
Advantages of Linear Optical EncodersLinear
Optical Encoders offer several advantages over other types of encoders. These include:
1. High accuracy and resolution: Linear Optical Encoders can provide high-resolution measurements, up to sub-micron levels. They can accurately measure linear displacement due to their high level of precision and repeatability.
2. Fast response time: Linear Optical Encoders are capable of fast data acquisition rates, with some devices capable of measuring several hundred thousand positions per second.
3. Low hysteresis: Hysteresis refers to the difference between the encoder’s actual position and the position reported by the encoder. Linear Optical Encoders have very low hysteresis, which makes them ideal for high-precision applications where accuracy is critical.
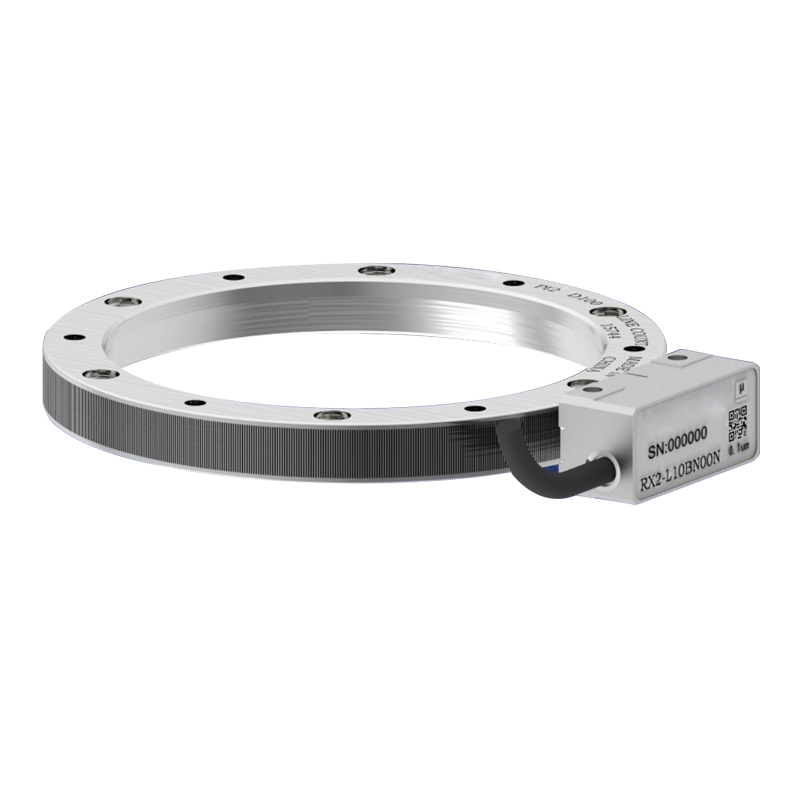

Applications of Linear Optical Encoders
Linear Optical Encoders find a wide range of applications in industries such as:
1. Manufacturing: In manufacturing processes, Linear Optical Encoders are used to monitor the position and movement of machine components, ensuring precise positioning and control.
2. Robotics: Linear Optical Encoders are used in robotics to provide accurate positional feedback for robotic arms, grippers, and other components.
3. Automation: In automated systems, Linear Optical Encoders are used to precisely measure the movement of conveyor belts, assembly lines, and other components.
ConclusionIn
conclusion, Linear Optical Encoders are high-precision devices that use the principle of optical interference to provide accurate measurements of linear displacement. They offer several advantages over other types of encoders, including high accuracy, fast response time, and low hysteresis. Linear Optical Encoders have a wide range of applications in industries such as robotics, automation, and manufacturing. As such, they are an essential tool for any industry that requires high-precision motion control.
If you have any questions about optical linear encoders, please contact us.
Whatsapp: 0086-13038878595
Wechat: Aico0905
Post time: Apr-12-2023